Hibernate is the best ORM (Object Relational Mapping) framework in Java. Let's understand how...
We are living in the world of software which is build using programming language e.g. Java. Software works with data. Data can be primitive values e.g int, float, string, double or in object (student object, employee object).
Student object will have 3 values and it should be stored somewhere (database).Database can be anything MySQL, Oracle, SQL server maybe Postgres, Adobe
Database is used to store data. The concept of storing data is called as persistence. Variables are transient which means we don't store data inside database directly.
To connect the java application with database, concepts of JDBC (Java database connectivity) is used. As we are using JDBC and have a database, we need SQL language now. But, not all developers are comfortable with SQL queries.
We need a solution to write data in DB without writing SQL queries.
class Student
{
roll no;
name;
marks;
}
Student studentObj and it can be directly store data in database by just writing save(studentObj) without writing SQL queries.
Here, ORM comes to rescue these developers and helps in storing data into database without using SQL.
How to convert java object into table?
As shown below, Class structure is similar to table structure. It can be achieved by creating relationship between Object Programming Language and Database system using ORM. ORM is a concept and to implement ORM we need some tool which is ORM tools e.g. hibernate, ibatis, JPA, Toplink etc.
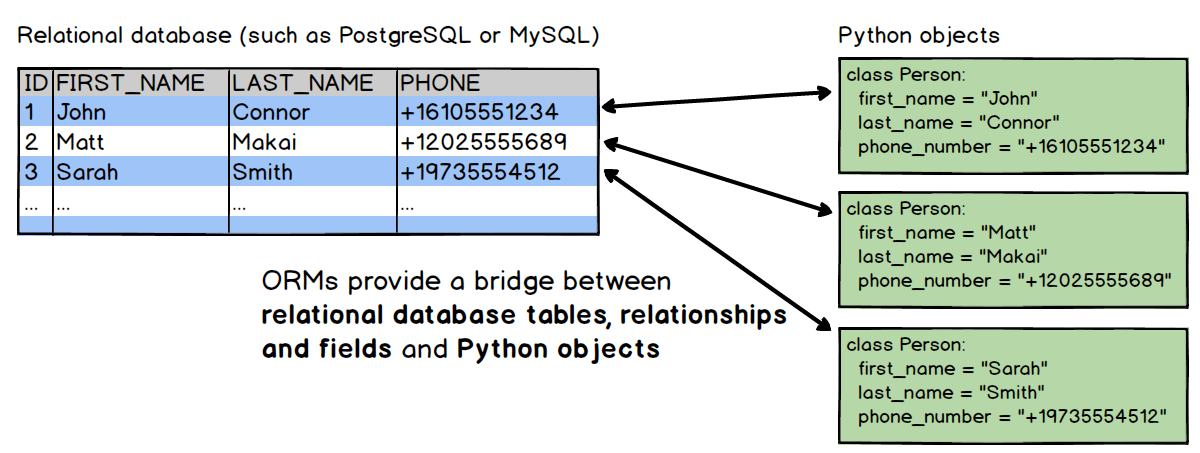
Using hibernate, objects can be stored into database directly using save(studentObj) method.
create SessionFactory -> create Session object -> session.save(studentObj)
Configuration of database needs to be provided in Session Factory like driver name, database url which is connect string, username, password and it can be done in different ways e.g. xml, java configuration.
















